Electric Braking of Dc Motor
Braking is usually employed
to stop or slow down the dc motor. Generally braking in dc machine is
classified as Electric Braking and Mechanical Braking. Generally,
electric braking is used to slow down the motor when motor goes slow down then
mechanical braking is applied to stop the motor at fixed position. Generally
electric braking is used in the application of dc motor where frequent or rapid
braking is required like train, hoist, metro train etc. The main principle of
electric braking is to apply negative torque as torque is directly proportional
to flux and armature current (T α ɸ.Ia) so torque can be
reversed by reversing the flux or armature current. Generally, Ia is
reversed. So when we apply electric braking then the motor tends to rotate in
opposite direction but we have to stop the motor so we have to apply mechanical
braking to stop the motor at final position.
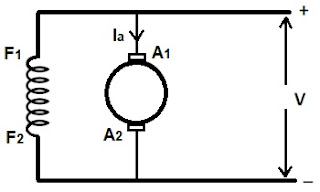
The above figure shown
represents the dc shunt machine working as motor. Now we will study the
different type of braking of motor referring to the above figure.
Types of Electric Braking in Dc Motor
There are three types of
braking of a dc motor these are
- Plugging
- Dynamic Braking
- Regenerative Braking
Plugging in Dc Motor
In this method armature terminals of motor (shunt motor or
separately excited motor) are reversed at the time
of braking. By reversing the armature terminals, the direction
of armature current is reversed. As the direction of armature current
is reversed then the direction of torque is also reversed (T α φ.Iₐ) this
reversed torque is known as braking torque. This braking torque will
reverse the direction of rotation and tends the motor to run in opposite
direction. In order to stop the motor at final position we need to apply
mechanical brakes. It is also known as Reverse
Current Braking.
In this method we did not change the direction of flux so direction of
supply voltage and induced voltage Eb (back emf) are same
therefore the voltage across the armature is V+Eb which is almost
twice the supply voltage.
The armature current is reversed
and a high braking torque is produced. In order to limit the armature current,
an external current limiting resistor is connected in series with the armature.
For braking of dc series motor
either the armature terminals or the field terminals are reversed.
Dynamic Braking of DC Motor
In dynamic braking, the
armature of dc motor is disconnected from supply and a braking resistor Rb is
immediately connected across the armature terminals and leaves the field
terminals connected to the supply. See if the field terminal is connected to
supply means flux(ɸ) is constant or in same direction and when the armature
terminals is disconnected from supply then armature is free to rotate in
constant flux and the dc motor work as dc generator and the direction of
armature current is reversed. As the direction of armature current is reversed
then the direction of torque is also reversed. Hence motor produces breaking
torque. It is also known as Rheostatic
Braking.
If breaking resistor is not
connected across the armature terminals, then the motor will take longer time
to stop. So for instant breaking, breaking resistor Rb is used.
For dynamic braking of dc
series motor, the field terminals of series motor is reversed and then the
motor is connected in series with braking resistor for instant braking.
Dynamic breaking is
inefficient method of braking, because all the energy is dissipate in
resistance.
Regenerative Breaking of dc Motor
It is the type of braking
in which kinetic energy of motor fed back to supply system. It is not an
intentional braking but it is an inherent property of motor i.e. when the motor
runs at a speed higher than its no load speed under constant excitation then
the motor back emf Eb is greater than the supply voltage, which
reverse the direction of armature current of motor. Then the dc machine
operates as dc generator and the energy generated is supply back to the source.
If the direction of armature current is reversed then the direction of torque
is also reversed and the machine produces braking torque.
Regenerative braking is
used where braking or slowing the motor is more frequent. It is most useful in
overhauling load. For example, when train is running at declined surface then
the speed of motor is greater than the no load speed of the motor and machine
produces the braking torque.
It wouldn’t stop the motor
but control the speed. It is used for controlling the speed above no load speed
of the motor.










No comments:
Post a Comment
Please feel free to provide feedback and suggestions, and also don't hesitate to ask your questions.