Dc Motor
Generally rotating machine contains
two parts the annular stationary part known as stator & the cylindrical rotatory
part is known as rotor, separated by a least possible air gap. The stator and
rotor are both made of ferromagnetic material (steel) which conducts the
magnetic flux upon which depends the process of energy conversion. Slots are
cut on the inner periphery of the stator and outer periphery of rotor
conductors are placed in the slots of stator and rotor. They are interconnected
to form winding. In dc machine field winding (concentrated type) is mounted on
stator and armature winding (distributed type) along with commutator is mounted
on rotor. The field poles are symmetrical and even in number, alternately north
and south.
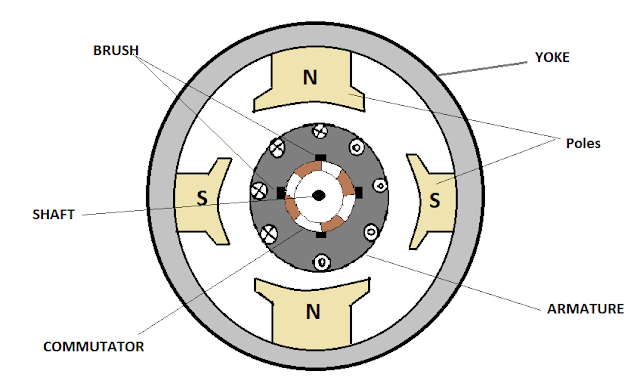
There are several parts of Dc machine
Yoke
Poles
Armature core
Commutator
Brush
Bearings
Shaft
Yoke
The yoke of a dc machine is an
annular ring which provides the mechanical support for poles and it also
provides the path for flux. In small dc motor yoke made from fabricated steel
and in special application (power electronics converter) laminated steel is
used.
Poles
The main field flux is created by
poles excited with direct current. There are two types of poles permanent
magnet poles and electromagnet poles. Steel laminations are provided to reduces
pulsation losses i.e. eddy current loss.
Pulsation losses
Due to teeths and slots on the outer
periphery of rotor flux distribution is non uniform i.e. flux is pulsating with
high frequency which creates eddy currents (called pulsation losses) in the
pole shoes
Armature core
Armature is center for
electromechanical energy conversion hence it should have high permeability. The
armature is made up of silicon steel with slots cut out on the periphery to
accommodate the insulated armature winding. The ends of each armature coil are
connected to the commutator segments to form a closed winding. To reduce eddy
current losses thin laminations are provided. Laminations are cut parallel to
flux direction
Brush
Brush is used to collect current from
rotating commutator and winding. The brushes are alternatively positive and
negative (electrical angle between adjacent pair being 1800). These
are placed in brush Holder with the spring for good mechanical conditions. DC motor brushes are made up of copper, carbon, electro-graphite, cu-graphite.
In order to have successful
commutation the brushes are physically placed along d axis to short circuit the
coil along q axis but schematically brushes are shown at q axis/MNA.
Bearing
The function of the
bearings is to reduce friction between the rotating and stationary parts of the
machine. Bearings support the armature which is mounted on the shaft.
Shaft
The shaft is made of mild steel. The rotating parts like armature core and commutator are mounted and keyed to the shaft.
Commutator
Commutator is a mechanical switch which converts
alternating voltage and current which are induced in armature in Dc and it is
also called mechanical rectifier. The commutator is cylindrical in shape and
comprises several wedge shapped copper segments bound together while they are
insulated from each other.








Nice Bro
ReplyDelete